Statistical Concepts of Six Sigma
Metric. A metric is a verifiable measurement of some particular characteristic, stated either numerically (for example percentage of defects) or in qualitative terms (for example, level of satisfaction-“poor” or *excellent). Me performance make decisions communicate with one another opportunities for employees, customers. suppliers and other stakeholders. Metrics are vital in six sigma application because they facilitate facts based decisions.
Six Sigma Began by stressing a common measure of quality. In Six Sigma terminology, a defect, or non-conformance, is any mistake or error that is passed onto the customer. A unit or work is the output of a process or an individual process step. A measure of output quality is defects per unit (DPU)
Defects per unit = Number of defects discovered/Number of units produced. However, this type of output measure lends to focus on the final products, not the process that produces the product In addition, it is difficult to use for processes of varying complexity, particularly service activities. Two different processes might have significantly different numbers of opportunities of error. making appropriate comparisons difficult. The Six Sigma concept redefined quality performance as defects per million opportunities (dpmo)
Dpmo = Number of defects discovered/opportunities foe error)A 1,000,000
For example, suppose that an airline wishes to measure the effectiveness of its baggage handling system. A DPU measure might be lost bags per customer. However, customers may have different numbers of bags, thus, total number of opportunities, for error is the average number bags per customer limes the number of customers. If the average number of bags per customer is 1.6, and the airlines recorded 3 lost bags for 8,000 passengers in one month, then there are (8,000)(1.6) opportunities for error, and
Dpmo – 3/(8,000) (1.6) A 1.000,000- 234,375
The use of dpmo allows us to define quality broadly. In the airline case, an “opportunity could be defined as every potential for failure to meet customer expectations from initial ticketing until bags are retrieved”. Thus, a failure to meet customer expectations might include excessive waiting time at the check-in, an incorrect reservation, a rude gate agent, or a delay in departure. This method provides a more comprehensive measure of potential failures that affect customer satisfaction.
| Types of Errors | Opportunity |
| Prescription | Miscalculation of dosage Wrong Drug Oral or written communication error |
| Dispensing | Misinterpretation of Rs Name confusion Poor labeling |
| Administration | Wrong time Wrong dosage Incorrect drug Wrong patient |
Metric such as dpmo, while used to teams addressing specific six sigma projects, need to be translated into the language of management-money. This translation provided the justification for selecting a Six Sigma project as well as appealing to top managers.
THE BELL SHAPPED, NORMAL, GAUSSIAN DISTRIBUTION
It can be shown under very general assumption that the distribution of independent random errors of observation takes on a normal distribution as the number of observations becomes large (Figure 1). Although others were involved, Gauss was one of the first to characterize this distribution and hence it is often named after him. It is also shaped like a bell, hence yet another name.
The height of the curve represent the probability of the measurement at the given distance away from the mean. The total area under the curve being one represents the fact that we are 100% certain (probability- 1.00) the measurement is somewhere.
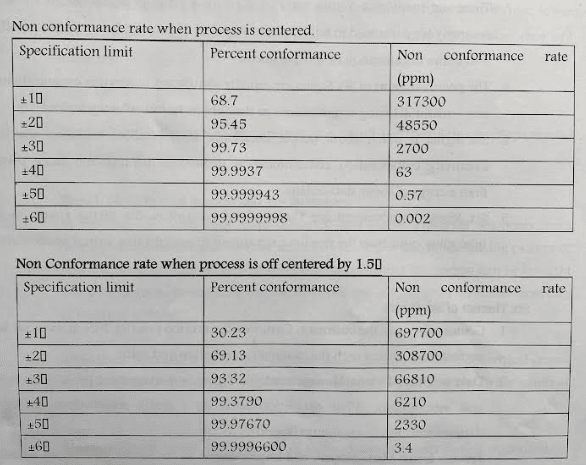
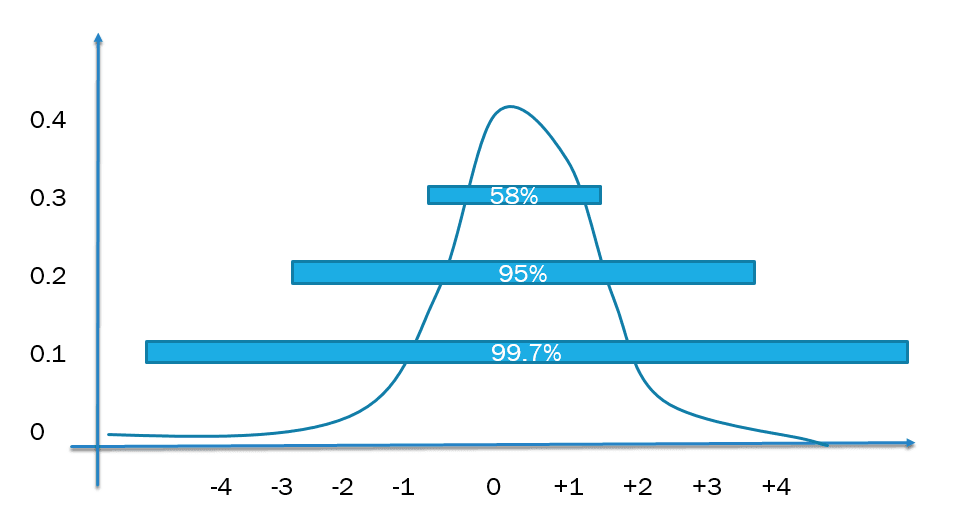
For a normal distributed data set, the empirical rule states that 68% of the data elements are within one standard deviation of the mean, 95% are within two standard deviation, and 99.7% are within three standard deviations. Graphically. this corresponds to the area under the curve as shown below for 1 and 2 standard devotions. The empirical rule of often stated simply as 68-95-99.7. Note how this ties in with the range rule of thumb, by stating that 95% of the data usually fails within two standard deviations of the mean(Figure 2).
Basic Assumptions
- Symmetrical distribution about he mean(bell-shaped curve)
- Commonly used in inferential stastistics
- Family of distributions characterized is by sigma and mean
From a measurement perspective, “Six Sigma” represents a quality level of at most 3 4 defects per million opportunities. From where did this concept arise? it stems from the notion of design specification in manufacturing and ability of a process to achieve specifications called process capability.
Process Capability
Process capability analysis entails comparing the performance of a process against its specifications. we say that a process is virtually all of the possible variable values fall within the specification limits
A capable process is one where almost all the measurement fall inside the specification limits.
This can be represented pictorially by normal; distribution curve.
The inherent variability of a quality characteristic that the process if capable of maintaining, when in a state of statistical control under a given set of conditions. Assuming normal distribution of the quality characteristic.
Process capability = + 3 SD = total spread of 6 SD.
Process capability is judge by comparing process performance with process requirements.
Since meeting specification limits is one of the most basic requirements of a process capability study, it is extremely important to accurately verify and define the specification limits.
Need for process capability
For meeting customer requirement/specifications.
To compare actual performance of equipment with manufacturer’s claim.
To compare the performance of two processes.
To provide more realistic tolerances for component dimensions.
Provide a basis for process control.
Factors influencing process capability
1. Condition of machine / equipment
2. Type of operation and operational conditions.
3. Raw materials.
4. Skill of operators.
5. Measurement method/ instruments.
6. Inspector’s skill.
Process capability indices, the Cp index
A major reason for quantifying process capability is ti compute the ability of a process to hold product tolerances. A measure of this relationship is process capability ratio or Cp Process capability is also known as potential capability.
The Cp index is given by.-
Cp = Tolerances/6 SD
Where tolerance = USL – LSL
SD- Standard deviation
Interpretations of Cp
Cp > 1. The Process is quite capable
Cp – 1, the process is just capable Cp < 1, the process is incapable
The recommended value of Cp is 1.33 (minimum)
In order to achieve Six Sigma quality in the organization, we must reduce the variation in the process so as to achieve the value of Cp=2
A Six Sigma quality level corresponds to a process variation equal to half the design tolerance while allowing the mean to shift as much as 1.5 standard deviations from the target.